INTRODUCTION TO ICT TRADING STRATEGY PDF GUIDE
Over the years, trading has undergone significant evolution, leading to the emergence of diverse trading approaches and strategies. While some strategies have flourished and proven to be highly successful, others have gradually faded away. Amidst this landscape, one trading strategy stands out for its dynamism, effectiveness, and the reactions it elicits from traders – the ICT Trading Strategy.
Our ICT Trading Strategy PDF guide aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this strategy, which encompasses technical analysis, market structure analysis, order flow dynamics, risk management, and psychological discipline. Traders who adhere to ICT’s teachings seek to adopt a structured and systematic approach to trading financial markets, with a primary focus on achieving consistency and profitability.
In this guide, we will dissect the ICT trading strategy, simplifying its concepts to make them easily understandable. Additionally, we will explore some of the best approaches developed within the ICT framework to strengthen your grasp of the strategy.
So, if you’re eager to learn from our ICT trading strategy PDF guide, grab yourself a refreshing drink, your notepad, pen, and personal computer as we embark on this insightful journey.
What is ICT Trading Strategy?
The Inner Circle Trader (ICT) Trading Strategy is a methodology designed to equip traders with a profound understanding of market dynamics, particularly focusing on market structure and the influence of institutional players on price movements. Unlike many other trading approaches that rely on numerous indicators, ICT trading emphasizes the use of raw price action.
This trading strategy, developed by a trader named Michael Huddleston, centres around the analysis of market movements from the perspective of “smart money” or institutional traders. By delving into the inner workings of these influential players, ICT trading seeks to provide traders with a comprehensive understanding of market behaviour.
To better grasp the ICT trading strategy, it’s crucial to explore the underlying concepts that form its foundation. By understanding these concepts and how they are applied in analyzing financial markets, traders can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of market movements.
ICT Trading Strategy PDF Guide (Basic Concepts)
ICT concepts refer to a collection of trading principles created to assist traders in making informed decisions within the financial markets. These concepts form the backbone of the ICT trading strategy. They encompass a range of principles aimed at providing traders with a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
In our ICT trading strategy pdf guide, we will delve into these fundamental ICT concepts, offering detailed explanations accompanied by practical illustrations. By exploring these concepts, traders can gain valuable insights into the underlying principles that drive the ICT trading strategy. Below, we outline some of the key ICT concepts that serve as pillars for effective trading.
Download Also: Smart Money Concept Trading PDF
.
.
.
SWING POINTS & LIQUIDITY
The first concept I will be writing about in this article is the swing points and the idea of liquidity. The very first thing we need to understand is the idea of swing points and their relation to liquidity. Swing points are either swing lows or swing highs. To identify swing points, we need three candles.
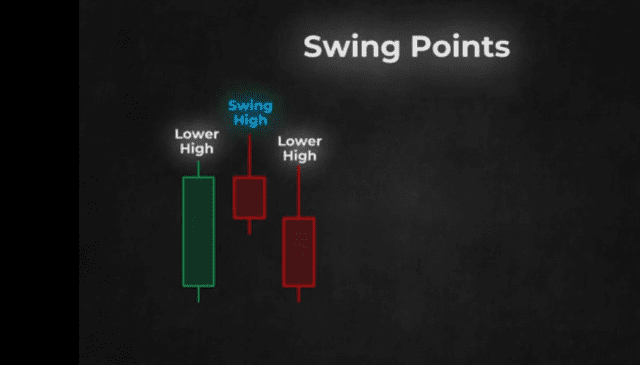
Looking at the diagram above you will see that in a swing high, the candle in the center has a lower high to the left and a lower high to the right.
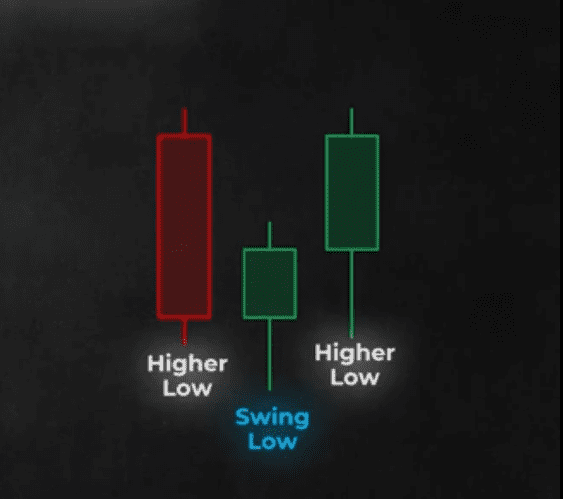
In a swing low, the candle in the centre has a higher low to the left and a higher low to the right as shown in the diagram above.
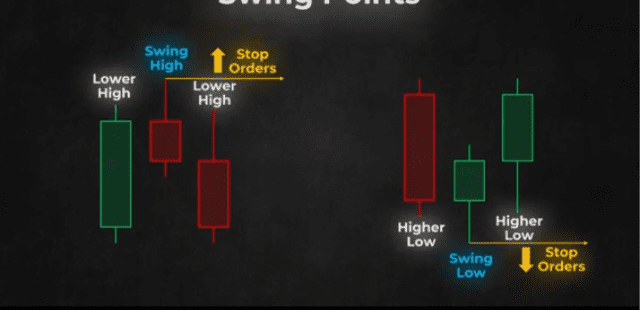
The reason the idea of swing points is important is that many retail traders place Stop orders just above swing highs or just below swing lows, meaning that liquidity is deeper in these areas.

You should know that in a long trade, the stop loss and the take profit targets are sell orders, and in a short trade, the stop loss and take profit targets are buy orders. This idea leads us directly to the concept of buy side and sell side liquidity.
BUY SIDE LIQUIDITY
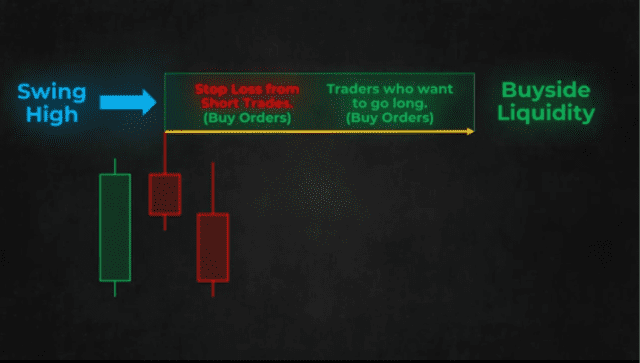
Looking at the diagram above you will see that just above a swing high there are a lot of stop orders from short trades which are buy-stop orders. And there are also a lot of buy-stop orders from traders who want to go long if the price surpasses the swing high. In ICT trading terms, this level represents buy-side liquidity.
Download ICT Trading Concept pdf
SELL SIDE LIQUIDITY
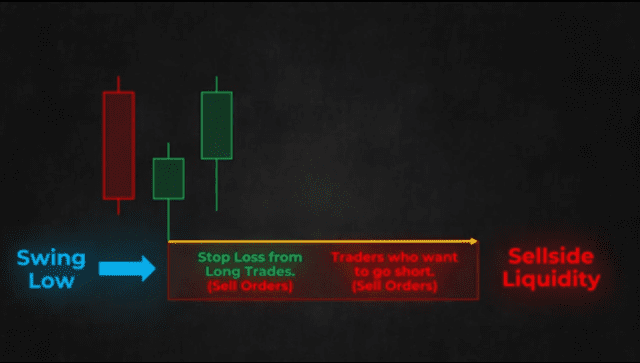
Again looking at the diagram above, just below a swing low there are a lot of stop loss orders from long trades which are sell-stop orders and there are also a lot of sell-stop orders from traders who want to go short if the price surpasses the swing low. In ICT trading terms, this level represents sell-side liquidity.
The identification of buy side and sell liquidity levels is important in many ways in the ICT trading strategy. Now that we already have an idea of what buy & sell side liquidity means, let’s move on to a real price chart and observe examples of buy-side and sell-side liquidity levels to better increase your understanding.
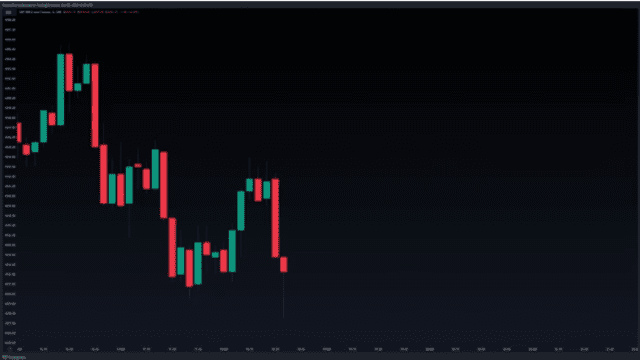
Looking at the 5-minute chart of the mini S and P, you can see that we currently have a low. This is a potential swing low because the candle to the left has a higher low. If the next candle produces a higher low, the current candle in the chart above will be classified as a swing low, which represents a point of sell-side liquidity.

Now, looking at the chart above we can see that the next candle that follows, is a higher low, so we can go ahead and classify the previous low candle as a swing low.
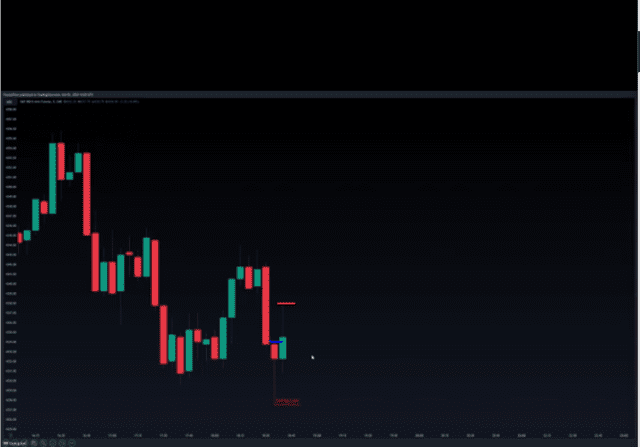
While we are paying attention to the swing low, notice that we also have the potential for a swing high in this candle. That’s because the candle to the left has a lower high as indicated by the blue line in the chart above when compared to the current candle. If the next candle also produces a lower high. Then the point indicated with the red line on the chart above will be classified as a swing high or buy side liquidity.

Looking at the chart above in the next candle, we can see that it produced a lower high as indicated by the blue line on the chart above, so we can go ahead and mark the previous green candle as a swing high. Again we have the potential to another swing low. If the next candle produces a higher low, we’ll have another swing low.
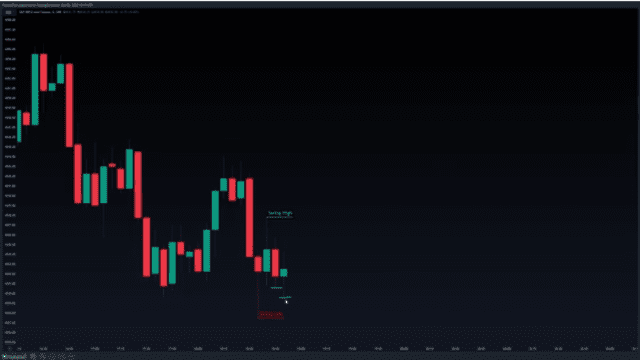
Looking at the next candle, we can see that it doesn’t happen, rather the new candle forms a lower low as you can see in the chart above. Now this new candle is a potential candidate for a swing low because it has a higher low to its left also.
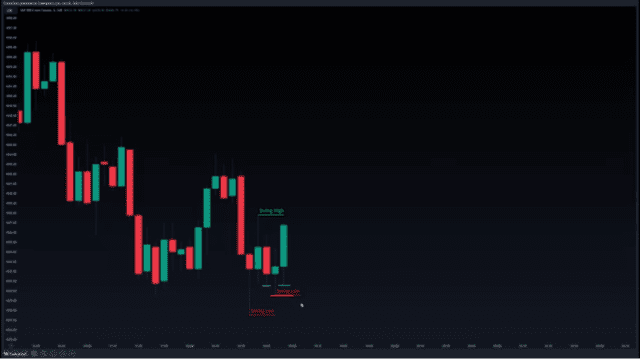
In the next candle, we can see that a new swing low forms, so we can go ahead and mark it out as shown on the chart.
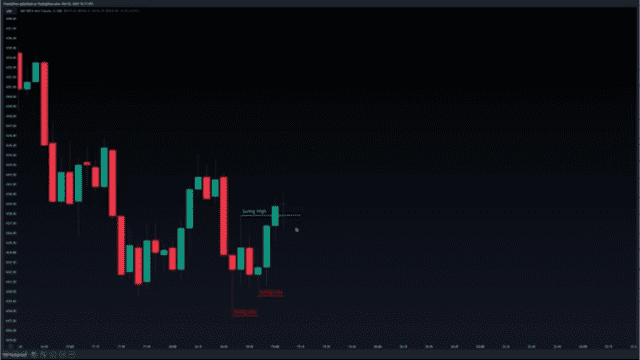
In the next 2 candles shown in the chart above, we can see that the price takes out the last swing high and comes back to test it on the other side as support.
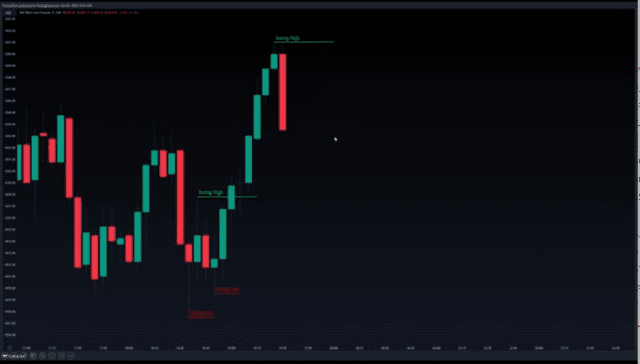
Over the next four candles, we can see that only higher highs and higher lows are formed. Eventually, price produces a candle with a lower high and renders the previous high as a swing high or buy side liquidity, so we can go ahead and mark it out.
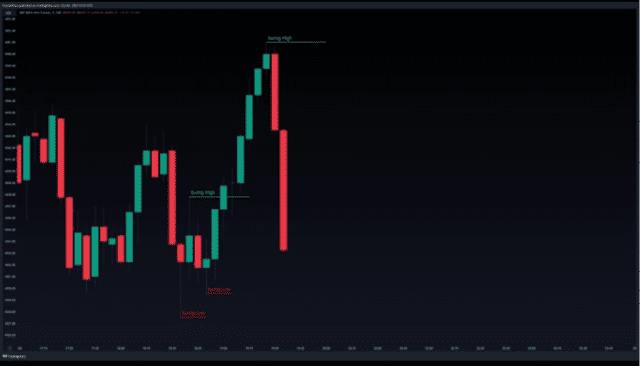
in the next candle. Price continues to the downside. You can see from these illustrations that identifying swing points is very simple, it’s also a good idea to practice it often in real-time, so it becomes very easy for you to identify or spot them.
Once you start to mark swing points in real price charts, you will notice that certain swing points cluster together while others remain isolated, giving rise to two distinct definitions of highs and lows called ‘equal highs & lows and old highs & lows.
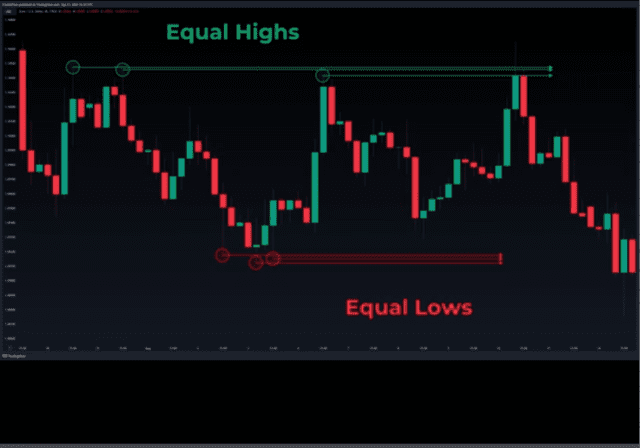
In the chart above, we can see an example of equal highs. Notice how three swing highs cluster together roughly at the same level, still in the same chart we can spot an example of equal lows. in this case, three swing lows cluster to form equal lows.
Notice that equal highs and lows don’t necessarily happen at the same price level perfectly. They simply cluster together in the same area.
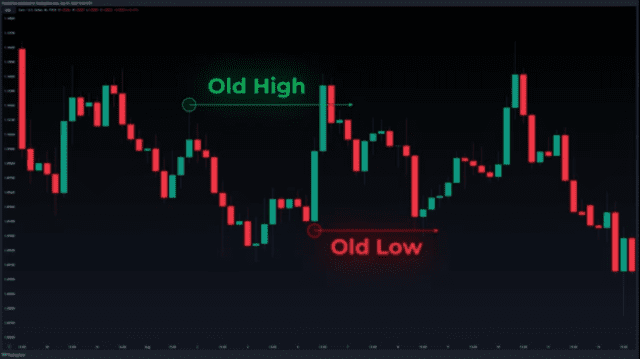
In the chart above, we can see the concept of old highs and old lows in the circled wicks/shadows, which are swing highs and lows that stand out or that are isolated in a way. Notice that in an example of the old low, price pierces the old low without closing below therefore forming a wick and then it starts to go up. This is an important discovery not only for the ICT Trading concepts but in the overall idea of market manipulation, meaning the triggering of liquidity to deceptively induce retail traders to one side of the market.
On the topic of highs and lows, we can look at other important types of highs and lows in any price chart, namely the previous week’s highs and lows the previous day’s highs or lows, the Trading session’s highs and lows or the even the intraday timeframe high and lows.
We’ll take another look at that when we talk about the concept of daily bias. The next ICT concept we will be looking at in ICT trading strategy is the idea of discounts in premium zones.
DISCOUNT & PREMIUM ZONES
You can also read the full article by clicking this link Here.
Download More Trading PDF Articles:
- 24 Powerful Candlestick Patterns PDF Guide
- Swing Trading Strategy PDF
- The Best Day Trading Strategy PDF Guide in 2024
- Taking Profitable Trades Using Trading Chart Patterns PDF Guide
- Supply and Demand Trading Strategy PDF Guide
- The Best Day Trading Strategy PDF Guide in 2024
Join our telegram community to get up-to-date news, educational materials, free online classes, market analysis, and crypto futures trade signals that will help you grow and become profitable.
Subscribe to our newsletter to get more educational content, tips, and updates.
This is very very useful for me my trading skills devoloping
We are glad you love it