Introduction
Price action refers to the behavioural pattern of the price of an instrument (commodities, currencies, stocks, cryptocurrencies, etc.) over a certain period. These price actions are mostly represented through the use of charts.
Price action trading, on the other hand, can be referred to as the process in which the traders use the price action data to analyze and speculate the potential or future direction of a particular instrument (commodities, currencies, stocks, cryptocurrencies, etc.). The traders are able to use the price movements and historical data shown on the chart to predict the future positions or direction of the market without the use of advanced trading indicators.
It is a popular and effective strategy for traders seeking to understand and profit from market movements. It’s an approach that relies basically on analyzing historical price data on the price charts to predict or speculate future price direction.
The trading community and environment have evolved over time, and with this, a lot of advanced trading and analytical methods. One of the most common methods in recent times has been the use of advanced trading indicators to help traders easily identify key factors in the market as well as to help them easily interpret market data.
That notwithstanding, the traditional methods of trading haven’t lost their utility, as they still seem to be one of the most basic and reliable ways of accurately analyzing market data. Price action trading is one of the traditional methods of trading, and it is still very reliable as the trader is able to understand using market basics, the behavioural patterns of the market participants, and how to easily use these patterns to make predictions and speculations without relying on modernized trading indicators.
Therefore, In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the world of price action trading into easy-to-understand segments, providing you with the knowledge and basic skills needed to become a successful price action trader.
Understanding Price Action Trading
One of the most basic aspects of price action trading is the use of charts, and there are three types of price charts used in price action trading:
Bar Charts
Bar charts are used to represent specific periods for trading. They provide more price information than line charts but not as much as the candlestick chart. Each bar chart represents one day of trading and contains the opening price, highest price, lowest price, and closing price for a trade. A dash on the left is the day’s opening price, and a similar dash on the right represents the closing price. Colors are sometimes used to indicate price movement, with green or white used for periods of rising prices and red or black for a period during which prices declined.
Line Charts
Line charts are used to detect a currency’s long-term patterns. They are the most basic form of chart for forex traders. They display the currency’s closing trading price for the periods provided by the user. A line chart’s trend lines can be utilized to develop trading strategies. For example, you may utilize trend line information to spot breakouts or changes in trends for increasing or falling prices.
A line chart, while informative, is often utilized as a starting point for additional trading research.
Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts are price indicators used in financial trading to represent the price movement of a financial instrument over a period of time. It also shows a clearer picture of price action and what is going on in the market. They are also a fundamental aspect of price action analysis. Imagine the price of an asset as a series of candles. Each candlestick reveals important information about price movement.
Basics of Candlestick Patterns
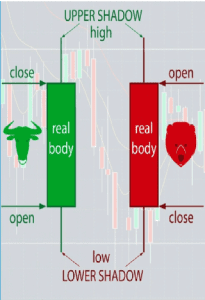
Candlestick charts are a visual representation of price data. Each candlestick has a body and wicks or shadows, representing the opening, closing, high, and low prices within a specified time frame.
Common Candlestick Patterns
Doji:
There is another single candlestick reversal pattern, which could be either bullish or bearish, depending on the combinations of the preceding and the subsequent candlestick formations.
Hammer:
This is a single candlestick reversal pattern made up of a small real body, ideally to be white/green but could be black/red, with a long lower shadow but a very short or even non-existent upper shadow.
Engulfing Pattern:
The Engulfing pattern is a reversal pattern that can be bearish or bullish. When it appears at the end of a downtrend, it would be a bullish engulfing pattern, and when it appears in an uptrending market, it would be a bearish engulfing pattern.
Interpretation of Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns provide insights into market sentiment. A hammer, for instance, suggests a potential bullish reversal, while a shooting star hints at a bearish reversal.
Uses of Candlestick Charts
Candlestick patterns provide deeper insights into price action for traders in the financial market.
In-depth analysis of Candlestick Patterns
Understanding individual candlestick patterns, such as doji, engulfing patterns, and hammers, morning and evening stars etc, gives the trader a piece of clearer market information. You are able to, at a glance, understand the market sentiment and identify the buy and sell pressure. To get a deeper understanding of the various candlesticks formation and how you can use these candlesticks to understand the price movement better, you can read the article on candlesticks.
Combining Candlestick Patterns with Other Price Action Signals
Candlestick patterns are even more powerful when used in conjunction with other signals. Read our article on candlesticks to understand better how to use them properly.
Real-World Examples of Candlestick Analysis
Examining historical charts to see how candlestick patterns played out in real trades is way easier with the candlesticks, as you are able to understand trends, selling and buying pressure, the presence of liquidity in the market, and other happenings in the market using candlestick charts.
Read Also: 7 Candlestick Patterns Every Trader Should Know
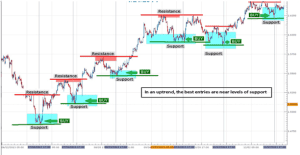
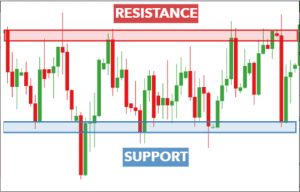
Support and Resistance Levels
Understanding support and resistance levels is crucial in price action trading. These levels are like invisible lines that influence price movement.
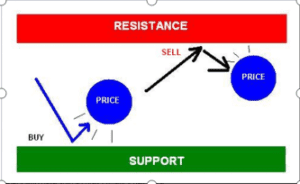
Support and resistance levels are fundamental technical analysis tools used by traders in financial markets. They are simple yet effective methods that enable traders to determine the direction of the market quickly, the best timing for market entry, and the ideal points for exiting a trade at either a profit or loss. By identifying support and resistance levels on a chart, traders can easily answer these questions and develop a sound trading idea.
Definition of Support and Resistance
Support:
A price level where demand is strong enough to prevent further price decline and pushes for an inclination or increase from that particular level. Support is a term used in finance to refer to the price level at which demand, or buying power, is strong enough to prevent the price of an asset from declining further.
The idea is that as the price approaches the support level, buyers see a better deal and are more likely to buy, while sellers become less likely to sell because they are getting a worse deal. This shift in supply and demand dynamics can result in demand overcoming supply, which can help to prevent the price from falling below the support level.
Resistance:
A price level where selling pressure is sufficient to halt upward price movement. Resistance is a key concept in technical analysis that refers to a price level where selling pressure is strong enough to prevent an asset’s price from rising further.
The idea behind this is that as the price approaches resistance, sellers may be more inclined to sell while buyers become less interested in buying, resulting in a stalemate in the market. This lack of buying pressure against the selling pressure means that the market may experience a reversal, and the price is unlikely to breach the resistance level.
Identifying Key Levels on a Price Chart
To identify these levels, examine historical price data. Look for areas where the price has repeatedly changed direction.
Role of Support and Resistance in Price Action Trading
Support and resistance levels help traders make informed decisions. Buying near support and selling near resistance is a common strategy. They can also be called supply and demand levels; as already explained earlier, the support levels can also be called demand zones, while the resistance levels can be called supply zones. To better understand support & resistance levels as well as supply and demand zones, you can read the article below.
Read Also: Supply and Demand Zones: A Profitable Trading Strategy
Reading Price Action Signals
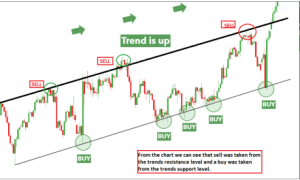
Trend Analysis
Price action trading involves analyzing trends, which are the general direction of price movement.
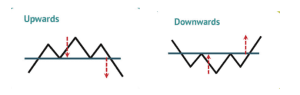
The trendline strategy utilizes the trendline as either support or resistance. A trend that goes on for a while tends to form a channel. In an uptrend, you have the higher highs (H.H) and the higher lows (H.L), while in a downtrend, you have the lower highs (L.H) and lower lows (L.L).
Identifying Trends
Uptrend: Higher highs and higher lows characterize an uptrend.
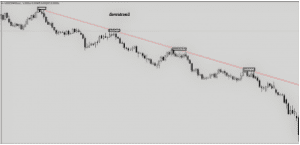
Downtrend: Lower highs and lower lows indicate a downtrend.
Sideways/Range: When prices move within a range, it’s a sideways or ranging market.
Trendlines and Their Significance
Trendlines help visualize trends. Drawing them connects the lows or highs in an uptrend or downtrend, respectively. As shown in the diagram above, drawing your trendlines also helps you in identifying the diagonal support and resistance levels. They can also be called pullback and continuation levels.
Trading with the Trend vs. Countertrend Trading
- Trading with the trend is less risky, as it follows the prevailing market sentiment, which is always better than going against the market flow. This is especially true for retail traders, as they don’t have the ability or the financial capacity to drive the market in their direction.
- Countertrend trading seeks to profit from trend reversals but is a lot riskier and is only beneficial for institutional traders and institutions with a large liquidity deposit.
To get a more in-depth understanding of trendlines analysis, you can click the link below to read the article.
Read Also: The Secret to Profitable Forex Trading: Trendlines and Channels
Price Patterns
Price patterns are specific formations that often repeat in the market and serve as an indication of an active price action. Many of the most effective price patterns occur when a trend is about to reverse or when there might be a possible dip or rise in price action. Some of the price patterns work both ways, doubling their usefulness.
Examples of Price Patterns
Head and Shoulders:
A reversal pattern with three peaks – the middle one is the highest. The head and shoulder pattern makes a shape that looks similar to a head and two shoulders. It is made up of a head pattern, which is either the highest in the case of a bearish reversal or the lowest in the case of a bullish reversal.
Double Tops/Bottoms:
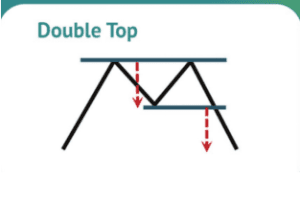 Reversal patterns indicating potential trend change. Double-top price patterns occur when a currency pair reaches the highest point, followed by a second attempt upwards. This, in turn, forms an “M” shape where a neckline emerges.
Reversal patterns indicating potential trend change. Double-top price patterns occur when a currency pair reaches the highest point, followed by a second attempt upwards. This, in turn, forms an “M” shape where a neckline emerges.
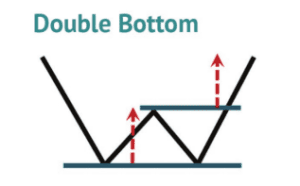 Double bottom price patterns occur when a currency pair reaches the lowest point, followed by a second attempt downwards. This, in turn, forms a “W” shape where a neckline emerges.
Double bottom price patterns occur when a currency pair reaches the lowest point, followed by a second attempt downwards. This, in turn, forms a “W” shape where a neckline emerges.
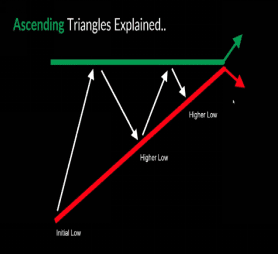
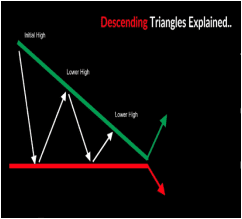
Triangles:
Continuation patterns that show a period of consolidation before a breakout. Triangles can also be referred to as currency wedges, and they appear when currency pairs start ranging, and prices start getting closer together. Once the pattern is broken, it can be a sign to buy or sell. There are two forms of triangles, namely, the ascending Triangle pattern and the descending triangle pattern.
Recognizing and Trading Price Patterns
Identifying these patterns involves understanding their shapes and what they signify. To better understand price patterns, their shapes, and what they represent in the market, you can read our article on price/chart patterns.
Read Also: 8 Chart Patterns Every Beginner Trader Must Know to Succeed in Trading
Key Price Action Trading Strategies & Techniques
Support and Resistance Trading
The best way to trade using the support and resistance levels is by Buying near support and selling near resistance.
Entry and Exit Techniques Using Support and Resistance
- Enter a trade when the price bounces off support or resistance. Ensure that you have a confirmation strategy. This can be in the form of candlestick patterns, chart patterns, and many others.
- Exit when price approaches the opposite level or when a breakout occurs. To exit the trade, you wait for the price to get to the next resistance level if you entered a buy trade and the next support level if you entered a selling trade.
Risk Management in Support and Resistance Trading
Using stop-loss orders to limit losses and position sizing to control risk, as usual, is very important. Therefore, you need to look for zones or levels below or above the points of entry, depending on the position you take, to place your STOP LOSS levels.
You should also have a proper lot size that you should use when entering market positions. This is largely dependent on your margin and liquidity.
Trend Following Strategies
Strategy Overview
Identifying and riding established trends is the best way to trade using the trend trading strategy; using the chart provided above, the trader needs to establish the trend direction before determining the position to enter.
2. Moving Averages and Trend Confirmation
Using moving averages to confirm trends and entry points. The moving average is one of the most traditional indicators used in trading, and they are also very helpful in identifying trends, as they help filter out the market noise. To learn more about the moving average indicator, you can read it through the link below.
Read Also: How to Use Moving Averages for Proper Price Analysis
Position Sizing and Risk Management for Trend Following
Calculating position sizes based on risk and volatility.
Breakout Trading
Strategy Overview
Trading the price breakout from a consolidation phase. Breakout trading is another price action trading strategy that lots of traders make use of. They are very effective when there has been a ranging trend for a long time.
2. Identifying and Trading Breakouts
Using technical analysis to spot breakout setups. To spot breakouts, finding ranging markets is the best option as the trader waits for the opportunity for the price to break out from a particular zone that it has been trading within, after which other confirmation patterns will be needed before entering your trade.
3. False Breakouts and Avoiding Traps
Recognizing and mitigating the risks of false breakouts. One of the pitfalls to avoid when trading breakouts is the false breakout trap. There are several ways to avoid these traps. To learn how to trade breakout you can click on the link below.
Read Also: Meaning of Breakout and how to trade them.
Reversal Trading
1. Strategy Overview
Catching trend reversals early for high-profit potential. Another great price action trading strategy is to identify when price action is about to change in opposite directions and take an early entry. This method needs a lot of experience and market analysis.
2. Recognizing Potential Reversals
Using candlestick patterns and divergence as reversal signals. Candlestick patterns and price/chart patterns are some of the methods used in identifying these reversals.
3. Trading with Reversal Patterns
Entering trades when reversal patterns confirm a change in trend.
Risk Management and Psychology in Price Action Trading
Risk Management
Importance of Risk Management in Price Action Trading
Avoiding large losses is crucial for long-term success.
Position Sizing and Stop-Loss Placement
Determining the appropriate position size and placing stop-loss orders.
Risk-reward ratios and Their Significance
Balancing risk and reward in every trade.
Trader Psychology
Emotions in Trading (Fear, Greed, Discipline)
Understanding how emotions can affect decision-making.
The Impact of Psychology on Trading Decisions
How fear and greed can lead to impulsive actions and losses.
Strategies for Maintaining Emotional Discipline
Practical tips to control emotions while trading.
Understanding risk management and trading psychology as a trader is one of the biggest ingredients needed for you to become a successful trader. Therefore, as a trader, you need to master the art of risk management. To learn all you need to know about risk management and trading psychology, you can read the article below.
Read Also: 3 Simple Forex Risk Management Strategies that Improve Profitable Trading
Practical Applications and Tools for Price Action Trading
Price Action Trading Tools
1. Charting Platforms and Software
Popular platforms like MetaTrader and TradingView. In order to access the market, you need a platform so you can see the price action represented through charts. Technical analysis can only be done with the use of price charts. Therefore, you need to get registered on a very reliable platform to begin price action trading.
2. Indicators and Tools that Complement Price Action Analysis
Although price action trading involves the use of trading without the use of trading indicators, some traditional or natural indicators, as I like to call them, can further strengthen the analysis of every trader. Using moving averages, Fibonacci retracement, and RSI alongside price action, in most cases, is more effective.
Advantages and Limitations of Price Action Trading
Advantages of Price Action Trading
1. Transparency and Simplicity
No reliance on complex indicators or algorithms.
2. Applicability to Various Asset Classes
Price action principles can be applied to stocks, currencies, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
3. Adaptability to Different Timeframes
Suitable for day traders and long-term investors alike.
Limitations of Price Action Trading
1. Subjectivity in Analysis
Different traders may interpret price action differently.
2. False Signals and Whipsaws
Price action isn’t foolproof; occasional false signals occur.
3. Continuous Learning and Practice Required
Becoming proficient in price action trading takes time and effort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, price action trading is a valuable approach for traders looking to gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics. By mastering the art of interpreting price movements and combining it with effective risk management and psychological discipline, traders can develop a robust foundation for success in the financial markets. Continuous learning, practice, and adaptability are key to thriving in the ever-evolving world of finance. Embrace price action trading, and you’ll be well on your way to becoming a more confident and profitable trader.
I hope you have found some value in this detailed article. Forex trading is a long process; as I always say, it’s a journey. Every trader is looking to discover new ways to become more profitable in the market. Thus, there is a need for more practice, research, and experimentation. Everything written here so far sums up some of the information and knowledge I have acquired in the market regarding price action trading.
Feel free to drop your contributions, questions, and suggestions, as I will attend them all. See you in the following article.
You can get this article in pdf format, click the button below to download the Price Action pdf format.
«« Download PDF »»